Product
Contact Us
Service Hotline:
E-mail:anxin@qilu-pharma.com
Company address: 10678 Wenliang Road, Dongjia Street, Licheng District, Jinan City, Shandong Province
Piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium
Banda preparation (piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium preparation) hotline: 0531-83126555 [drug name] generic name: piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium for injection commodity name: Banda English name: Piperacillin sodium and Tazobactam sodium for Injection pinyin: Zhusheyong Pailaxilinna Tazuobatanna [ingredient] this product is a compound preparation, its components are piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium. 0.5625g each respectively
Key words:
Detailed Description
Banda preparation (piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium preparation) hotline: 0531-83126555
[Name of Drug]
Common Name: Piperacillin Sodium and Tazobactam Sodium for Injection
commodity name: Banda
英文名称:Piperacillin Sodium and Tazobactam Sodium for Injection
汉语拼音:Zhusheyong Pailaxilinna Tazuobatanna
[Ingredient]
This product is a compound preparation, its components are: piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium. 0.5625g each contains 0.5g of piperacillin and 62.5mg of tazobactam respectively. Each 1.125g contains 1.0g of piperacillin and 0.125g of tazobactam respectively.
Chemical structural formula:
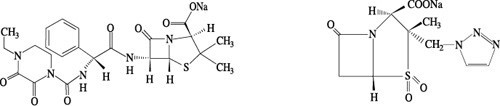
Molecular formula: C23H26N5NaO7S C10H11N4NaO5S
Molecular weight: 539.54 322.30
[trait]
This product is white or white loose block or powder; odorless, bitter taste, very hygroscopic.
[Indications]
This product is suitable for piperacillin-resistant, but piperacillin/tazobactam-sensitive beta-lactamase-producing bacteria caused by moderate to severe infections:
1. Appendicitis (with perforation or abscess) and peritonitis caused by piperacillin-resistant, β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Bacteroides (Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides ovale, Bacteroides pleomorpha or Bacteroides vulgare).
2. Uncomplicated and complicated skin and soft tissue infections caused by piperacillin-resistant, β-lactamase-producing Staphylococcus aureus, including cellulitis, skin abscess, ischemic or diabetic foot infections.
3. Postpartum endometritis or pelvic inflammatory disease caused by piperacillin-resistant, β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli.
4. Community-acquired pneumonia caused by piperacillin-resistant, β-lactamase-producing Haemophilus influenzae (moderate only).
Moderate to severe hospital-acquired pneumonia (nosocomial pneumonia) caused by piperacillin-resistant, β-lactamase-producing Staphylococcus aureus. Treatment of systemic and/or local bacterial infections caused by sensitive bacteria.
[Specifications] 0.5625g (including piperacillin 0.5g, tazobactam 62.5mg);1.125g (including piperacillin 1.0g, tazobactam 0.125g)
[Dosage]
An appropriate amount of this product is fully dissolved in 20 ml of diluent (0.9% sodium chloride injection or sterile water for injection), and then immediately added into 250ml of liquid (5% glucose injection or 0.9% sodium chloride injection) for intravenous drip for at least 30 minutes each time. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. Hospital-acquired pneumonia treatment for 7 to 14 days. And can be adjusted according to the condition and bacteriological examination results.
For adults with normal renal function (creatinine clearance> 90 ml/min) and children over 12 years of age, 3.375g (containing 3g of piperacillin and 0.375g of tazobactam) is given intravenously every 6 hours. In the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia, the initial dose is 3.375g once, once every 4 hours, and aminoglycosides are used in combination. If Pseudomonas aeruginosa is not isolated, aminoglycosides can be stopped according to the degree of infection and the condition.
For patients with renal insufficiency, the dosage of recommend is shown in the table below:
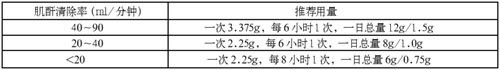
For hemodialysis patients, the maximum dose is 2.25g once every 8 hours, and 0.75g can be added after each hemodialysis.
[Adverse reaction]
1. The common adverse reactions of this product are:
(1) Skin reactions: rash, itching, etc.
(2) gastrointestinal reactions: such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, etc.
(3) Allergic reactions.
(4) Local reactions: such as injection of local irritation, pain, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis and edema.
(5) Other reactions: such as thrombocytopenia, pancreatitis, fever, fever with eosinophilia, elevated serum aminotransferase, etc.; these reactions occur when this product is combined with aminoglycosides.
2. In addition, the following adverse reactions can be seen in this product:
(1) diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, indigestion, etc.
(2) maculopapular rash, herpes, urticaria, eczema, etc.
(3) irritability, dizziness, anxiety, etc.
(4) Other reactions: such as rhinitis, dyspnea, etc.
[Taboo]
People who are allergic to penicillins, cephalosporins or beta-lactamase inhibitors are contraindicated.
[Note]
1. Penicillin skin test must be done before medication, and those with positive results are prohibited.
2. Cross allergic reactions: those who are allergic to cephalosporins, cephalosporins, griseofulvin or penicillamine can also be allergic to this product, and those who are allergic to a penicillin may also be allergic to other penicillins, so those who have a history of penicillin allergy should avoid using this product.
3. Patients with allergy history, bleeding history, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's enteritis or antibiotic related enteritis should be used with caution; patients with renal dysfunction should be appropriately reduced. (See Usage and Dosage)
4. This product contains sodium. When using this product in patients who need to control salt intake, serum electrolyte levels should be checked regularly: For patients who receive cytotoxic drugs or diuretics at the same time, be alert to the possibility of hypokalemia.
5. The coagulation time should be measured before or during the application of this product in patients with renal dysfunction. Once bleeding occurs, it should be discontinued.
Patients with pseudomembranous enteritis should undergo stool examination, culture for Clostridium difficile, and analysis of cytotoxins.
7. Patients with hepatic and renal insufficiency should monitor the concentration of piperacillin to adjust the dose.
Hematopoietic function should be checked regularly, especially for patients with a course of treatment ≥ 21 days.
The existing clinical research data show that this product is not effective in the treatment of lower respiratory tract infection and complicated urinary tract infection in hospital.
10. Interference to diagnosis: Direct antiglobulin (Coombs) test can be positive during the application of this product, and elevated blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine, hypernatremia, hypokalemia, elevated serum aminotransferase and serum lactate dehydrogenase, and increased serum bilirubin can also occur.
[Medication for pregnant and lactating women]
Pregnant women with caution. A small amount of piperacillin can be excreted from breast milk, causing sensitization of infants, diarrhea, candida infection and skin rash, so lactating women should suspend breastfeeding when applying this product.
[Use in children] The safety and effectiveness of this product in children under 12 years of age is unknown.
[Elderly medication] Elderly patients with renal dysfunction, should be appropriate to adjust the dose.
[Drug interactions]
1. This product has no synergistic effect on Enterococcus faecalis combined with gentamicin. In combination with certain cephalosporins, it also has a synergistic effect on some sensitive strains of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella, and Proteus.
2. In vitro tests, this product can be used in combination with aminoglycosides to inactivate aminoglycosides. When this product is combined with tobramycin, the area under the curve, renal clearance and urinary excretion of tobramycin will decrease by 11%, 32% and 38% respectively due to the inactivation of tobramycin by piperacillin-tazobactam. In patients with severe renal insufficiency, such as those on hemodialysis, when tobramycin is combined with piperacillin, the pharmacokinetics of the former will change.
3. This product can prolong the half-life of piperacillin by 21% and the half-life of tazobactam by 71% when combined with probenecid.
4. Piperacillin, like carbenicillin, azlocillin, mezlocillin and ticarcillin, when combined with drugs that can produce low prothrombin, thrombocytopenia, gastrointestinal ulceration or bleeding, may increase the risk of coagulation dysfunction and bleeding. For example, anticoagulants: heparin, coumarin, indandione; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics, especially aspirin, diflunisal and other salicylic acid preparations, other platelet aggregation inhibitors or sulfinazone.
5. This product should not be mixed with other drugs in syringes or infusion bottles. When used with other antibiotics, they must be given separately. Do not mix with solutions containing only sodium bicarbonate, and do not add blood products and protein hydrolysates.
[Overdose]
As with other penicillins, if administered intravenously and in excess of the recommend dose, the patient may experience neuromuscular excitement or convulsions.
[Pharmacology and Toxicology]
Piperacillin is a semi-synthetic penicillin antibiotic and tazobactam is a β-lactamase inhibitor. This product has antibacterial effect on piperacillin-sensitive bacteria and the following bacteria that produce β-lactamase and are resistant to piperacillin:
Gram-negative bacteria: Most of the following plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase-producing and non-producing bacteria: escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp (Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae), Proteus spp (Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris), Salmonella spp bacteria. Chromosome-mediated β-lactamase-producing and non-producing bacteria of the following species: C. flaudine, C. heterocitrate, Pruvidens, C. moerrhizae, Serratia (Serratia Marcescens, Serratia hydophila), P. aeruginosa and other Pseudomonas (P. cepacia, P. fluorescens, P. maltophilia), Acinophila.
Gram-positive bacteria: the following bacteria that produce and do not produce beta-lactamases: streptococcus (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus bovis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus viridis, Group C and Group G Streptococcus), Enterococcus (Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium), Staphylococcus aureus (excluding MRSA), Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Staphylococcus epidermidis (coagulase-negative staphylococcus), Corysis.
Anaerobic bacteria: the following bacteria that produce and do not produce beta-lactamases: bacteroides (Bacteroides, Bacteroides, Trichobacterium, Bacteroides melanin, Bacteroides oral), Bacteroides fragilis (Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides vulgaris, Bacteroides oides ovalis, Bacteroides pleomorpha, Bacteroides monomorpha, Bacteroides, Bacteroides dissolvus), Streptococcus pepticus, Clostridium (Clostridium difficum, Clostridium actinomycetes.
[Pharmacokinetics]
After intravenous infusion of this product, the plasma concentrations of piperacillin and tazobactam quickly reached peak values. After 30 minutes of infusion, the plasma concentration of piperacillin was equal to the plasma concentration of piperacillin given the same dose. When 2.25g, 3.375g and 4.5g piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium were injected intravenously for 30 minutes, the plasma peak concentrations (Cmax) of piperacillin were 134, 242 and 298 mg/L respectively, and the peak concentrations (Cmax) of tazobactam were 15, 24 and 34mg/L respectively.
The blood elimination half-lives (t1/2) of piperacillin and tazobactam ranged from 0.7 to 1.2 hours after single or multiple doses of piperacillin sodium and tazobactam sodium in healthy subjects, independent of dose and time of administration. Piperacillin is metabolized in the body into tiny biologically active de-ethyl metabolites, tazobactam is metabolized into products without pharmacological and antibacterial activity, and both piperacillin and tazobactam are excreted by the kidneys. 68% of piperacillin is rapidly excreted in the original form from the urine; tazobactam and its metabolites are mainly excreted through the kidneys, of which 80% are the original form. Piperacillin, tazobactam, and desethylpiperacillin can also be secreted through bile. About 30% of piperacillin and tazobactam are bound to plasma proteins, and their binding rate is not affected by other compounds; the binding of plasma proteins to tazobactam metabolites is negligible.
Piperacillin and tazobactam are widely distributed in tissues and body fluids, including gastrointestinal mucosa, gallbladder, lung, female reproductive organs (uterus, ovary, fallopian tube), body fluids, and bile. The drug concentration in the tissue is about 50% to 100 of the plasma concentration. As with other penicillins, cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of piperacillin and tazobactam are low in non-inflammatory lesions of the meninges. The blood elimination half-lives of piperacillin and tazobactam in patients with renal impairment are prolonged with decreasing creatinine clearance. When the creatinine clearance rate is less than 20 ml/min, the blood elimination half-life of piperacillin is 2 times that of normal people, and the blood elimination half-life of tazobactam is 4 times that of normal people.
Hemodialysis can remove 30% to 40% of piperacillin and tazobactam, and another 5% of tazobactam is removed by dialysis. Peritoneal dialysis removes 6% of piperacillin and 21% of tazobactam, up to 16% of tazobactam as metabolites. The blood elimination half-lives of piperacillin and tazobactam were prolonged by 25% and 18%, respectively, in cirrhotic patients compared with normal subjects, but no dose adjustment was required.
[Storage] Shaded, airtight, in a cool dark (not more than 20 ℃) dry place.
[packaging] glass bottle packaging, 5/box.
[Period of validity] 24 months.
[Implementation Standard] "Chinese Pharmacopoeia" 2010 Edition First Supplement
[Approval Document No.] Chinese Medicine Zhunzi H19990181; Chinese Medicine Zhunzi H19990182
Related Products